Glomerular Filtration Rate (1)
Tags | |
UUID | e19b8386-2de9-11e4-b7aa-bc764e2038f2 |
The Glomerular Filtration Rate calculator computes the flow rate of filtered fluid passing through the kidney.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
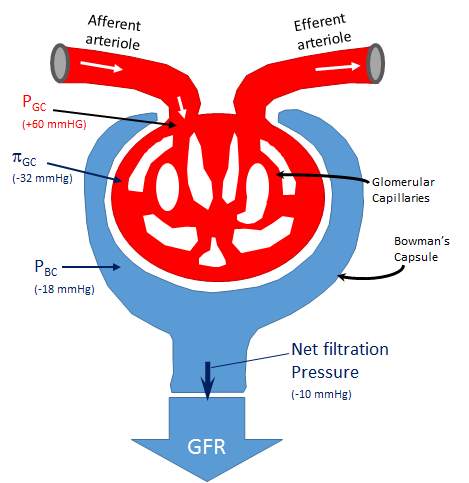
- (PGC) Glomerular Pressure
- (PBC) Bowman’s Capsule Pressure
- (PiGC) Glomerular Oncotic Pressure (also known as colloid osmotic pressure)
- (Kf) Filtration coefficient [Units: mL / (mmHg * minute) ]
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): The filter rate is returned in milliliters per minute (mL/min). However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The Glomerular Filtration Rate equation computes the flow rate of filtered fluid passing through the kidney. The GFR is a metric used in characterization of the level of kidney function. The GFR is used to identify stages of kidney disease as shown in the tabl ebelow: Stages of Kidney Disease. Specifically, the GFR estimates how much glomerular filtrate is formed in all nephrons of both kidneys per minute.
Glomeruli are the tiny filters in the kidneys that filter waste from the blood. The formula for the Glomerular filtration rate is:
GFR = Kf *((PGC - PBC)- PiGS)
where:
- GFR - Glomerular Filtration Rate
- PGC - Glomerular Pressure, the pressure in the glomerular capillaries that are enclosed in the Bowman's capsule
- PBC - Bowman’s Capsule Pressure, the fluid pressure in the Bowman's capsule
- PiGC - Glomerular Oncotic Pressure (also known as colloid osmotic pressure), the osmotic pressure tending to pull water into the glomerular capillaries, into the circulatory system
- Kf - Filtration coefficient
The average GFR is around 125 ml/min
Notes
The following table depicts the stages of Kidney Disease, showing the relative values for the Glomerular Filtration Rate associated with each stage. The lower the number the more damage has been done to the kidneys at progressive stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD).
STAGES OF KIDNEY DISEASE
| (CKD) | Description | GFR (mL/min) |
| Normal | Normal kidney function in this range of GFR | Approx 125 |
| 1 | Normal kidney function but urine findings or structural abnormalities or genetic trait point to kidney disease | More than 90 |
| 2 | Kidney damage and mild decrease in GFR | 60 to 89 |
| 3 | Moderate decrease in GFR | 30 to 59 |
| 4 | Severe decrease in GFR | 15 to 29 |
| 5 | Kidney failure (dialysis or kidney transplant needed) | Less than 15 |
FILTRATION COEFFICIENT
The filtration coefficient is a proportionality constant representing the average flow rate generated by the net filtration pressure. Since the inputs for PGC, Π, and PBC are units pf pressure, the filtration coefficient Kf must be in units of volumetric flow rate / pressure.
Examining the units of the filtration coefficient:
Net filtration pressure * filtration coefficient = volumetric flow rate
mmHG * Kf = mL/min => `kf has units of mL/(mmHG*min)
In our graphical example, the average GFR is around 125 ml/min and the notional net filtration pressure is around 10 mmHG
kf approx ("125 mL"/min) / 10 mmHG = 12.5 mL/ (mmHG * min)
vCalc content is available under the Creative Common Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. vCalc also provides terms of use and a privacy policy.
Equations and Data Items
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
